Startup Phases Explained: From Ideation to Impact
Embarking on the entrepreneurial journey is a thrilling yet challenging endeavor, marked by distinct phases that characterize the evolution of a startup. Each stage presents its own set of hurdles and opportunities, demanding adaptability, resilience, and strategic thinking. In this exploration, we dive into the nuanced definition of startup stages, shedding light on the dynamic nature of each phase.
|
Table of Contents |
Definition of Startup Stages
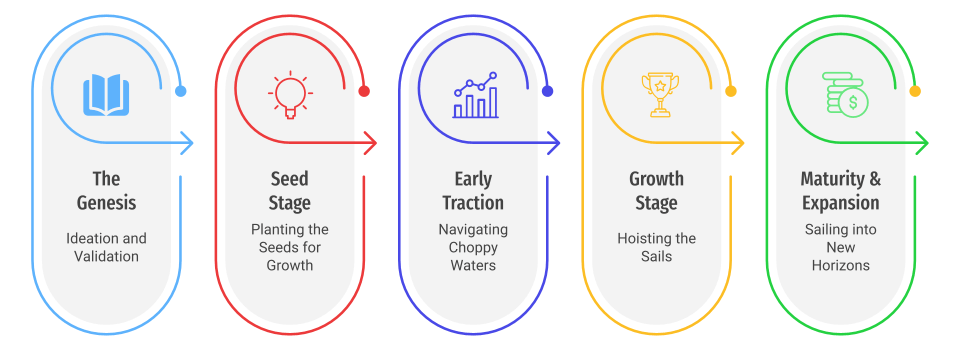
I. The Genesis: Ideation and Validation
The inception of a startup is rooted in ideation and validation. Entrepreneurs embark on this stage by identifying a problem or need, crafting a unique value proposition, and conducting meticulous market research. The emphasis lies on understanding the target audience, validating demand for the proposed product or service, and crafting a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) for iterative improvement.
II. Seed Stage: Planting the Seeds for Growth
As the startup gains momentum, the seed stage comes into play. This phase involves the formation of a founding team, the development of a comprehensive business plan outlining the business model and financial projections, and the initiation of fundraising efforts. Entrepreneurs may opt for bootstrapping, seek self-funding, or attract investors like angels or venture capital to lay the foundation for future growth.
III. Early Traction: Navigating Choppy Waters
The early traction phase marks the transition from ideation to implementation. Entrepreneurs focus on product development and refinement based on user feedback, scaling production or service delivery, and implementing marketing and sales strategies. In this stage you are looking to acquire first customers to better understand market demand with LOIs, pre-sales, waitlist growth, alpha-community. These serve as proxies for further derisking of the venture.
IV. Growth Stage: Hoisting the Sails
With a solid foundation in place, startups enter the growth stage, characterized by scaling the customer base, exploring new markets, and enhancing product or service offerings. This phase demands a strategic marketing approach, adapting to changing market demands, and securing additional funding through avenues like venture capital or strategic partnerships.
V. Maturity and Expansion: Sailing into New Horizons
As startups mature, they face the challenges of consolidating market share and exploring new business lines or markets. Operational efficiency becomes paramount, requiring the streamlining of internal processes and substantial investments in technology and infrastructure. Strategic partnerships and acquisitions may also play a pivotal role in propelling the startup into new horizons.
Stage 1: Ideation and Validation
Defining the Business Idea:
Every thriving startup starts with a well-thought-out business idea. Entrepreneurs must clearly express their vision, explaining the problem or need their product addresses. Successful startups emerge from a keen understanding of market problems. To identify problems, entrepreneurs observe their surroundings and look for problems that they can tackle with creative solutions.
Developing a Unique Value Proposition:
With the problem identified, the next challenge is to differentiate the startup from the competition. Crafting a unique value proposition is the key. This involves defining what makes the product or service stand out, how it addresses the identified problem uniquely, and why customers should choose it over existing solutions.
Market Research and Validation:
Ideas are only as good as their reception in the market. To transform a vision into reality, entrepreneurs must validate and understand their potential market. This involves an analysis of the industry landscape, competitor offerings, and potential challenges. Market validation ensures that there is a genuine demand for the proposed solution.
Target Audience Identification:
Understanding your target group is of the utmost importance. Entrepreneurs need to identify the demographics, preferences, and behaviors of their potential customers. This knowledge forms the basis for effective marketing strategies and ensures that the product resonates with the intended consumer base. A key method for this is customer development through discovery calls, which helps refine the ideal customer profile (ICP).
Building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP):
In the world of startups, it's often better to show than to tell. Building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is the next logical step. This stripped-down version of the product allows entrepreneurs to test their concept in the real world with minimal resources, providing tangible evidence of its feasibility. For the creation of the MVP focus on the most important key features only and cut of “unnecessary” features. In the beginning, simple mockups or wireframes in Figma might serve to get customer feedback as well.
Gathering Feedback for Improvement:
No product is perfect from the get-go. Gathering feedback from users interacting with the MVP or prototype is invaluable. It provides insights into user experience, functionality, and potential areas for improvement. This iterative process is fundamental to honing the product and ensuring it meets the needs of the target audience.
Stage 2: Seed Stage
The Seed Stage marks a critical juncture where the entrepreneurial journey takes shape. This phase is characterized by the formation of a solid foundation, the cultivation of a visionary team, and the strategic development of a roadmap for success.
Identifying Key Team Members:
Every member of the founding team plays a pivotal role. Identifying individuals with expertise in areas such as product development, marketing, finance, and operations is essential. These key team members contribute their unique skills and perspectives to build a well-rounded and capable foundation.
Defining Roles and Responsibilities:
Clarity in roles and responsibilities is the bedrock of a well-functioning team. Entrepreneurs must define each team member's role, ensuring that everyone understands their contributions and responsibilities. This not only fosters accountability but also creates an environment conducive to effective collaboration.
Developing a Business Plan:
With the team in place, the next step is the development of a comprehensive business plan. This document serves as the roadmap for the startup, outlining its mission, vision, and objectives. A well-crafted business plan also includes strategies for growth, market analysis, and a clear understanding of the competitive landscape.
Outlining the Business Model:
The business model is the mechanism that transforms the startup's vision into a sustainable and profitable venture. Entrepreneurs must outline how the company will create, deliver, and capture value. This involves defining the target market, revenue streams, and the unique value proposition that sets the business apart.
Creating Financial Projections:
Financial foresight is vital in the Seed Stage. Entrepreneurs must create realistic and data-driven financial projections, including revenue forecasts, expense estimates, and cash flow analysis. This not only aids in strategic decision-making but also proves crucial when seeking funding from external sources.
Fundraising:
The Seed Stage often necessitates external funding to bring the startup's vision to life. Entrepreneurs explore various avenues for fundraising, balancing the need for capital with the preservation of equity. Two primary methods at this stage are bootstrapping and self-funding or attracting angel investors and seed funding.
Bootstrapping and Self-funding:
Bootstrapping involves financing the startup with personal savings or revenue generated by the business itself. Self-funding, on the other hand, entails using personal or family funds to fuel initial growth. These methods provide autonomy but may limit the scale of operations.
Attracting Angel Investors or Seed Funding:
For startups with ambitious growth plans, attracting external investors becomes a strategic move. Angel investors and seed funding offer capital infusion in exchange for equity, providing the financial backing needed to scale operations, develop the product, and enter the market more aggressively.
Stage 3: Early Traction
This phase is marked by dynamic activities aimed at gaining momentum in the market. Startups move from development to a strategic push for customer acquisition and operational scalability.
Iterating Based on User Feedback:
User feedback is the North Star guiding product refinement. Startups must actively seek and embrace feedback from early adopters. This iterative loop of feedback and adjustment not only enhances the product but also fosters a user-centric approach, laying the foundation for customer loyalty.
Customer Acquisition:
Early Traction is synonymous with customer acquisition. Startups must implement targeted marketing and sales strategies to attract and retain customers. Understanding the needs and pain points of the target audience is crucial for crafting compelling value propositions and effective messaging. In addition, startups should think about how they can retain the customers they have acquired in order to save costs in the long term.
Implementing Marketing and Sales Strategies:
Marketing and sales strategies play a pivotal role in gaining traction. Entrepreneurs need to identify the most effective channels to reach their audience, whether it be through digital marketing, content creation, social media, or traditional methods. A well-crafted sales strategy complements marketing efforts, converting interest into tangible sales.
Building Brand Awareness:
In a crowded market, building brand awareness is paramount. Startups must create a distinctive brand identity that resonates with their target audience. Consistent messaging, a compelling brand story, and memorable visuals contribute to a strong brand presence, fostering trust and recognition.
Expanding Team as Needed:
Scaling operations often necessitates expanding the team. Entrepreneurs must strategically recruit individuals with the skills and expertise required to fuel continued growth. Building a cohesive and agile team is essential for navigating the challenges inherent in scaling a startup.
Stage 4: Growth Stage
This phase is characterized by dynamic activities aimed at scaling the customer base, diversifying offerings, and securing the necessary resources for sustained growth.
Scaling the Customer Base:
At the core of the Growth Stage lies the imperative to scale the customer base. Entrepreneurs leverage the momentum gained in the Early Traction phase to reach a broader audience. This involves not only retaining existing customers but also implementing strategies to attract new ones, fostering a robust and loyal customer community.
Expanding Marketing Efforts:
With an eye on growth, marketing efforts take center stage. Startups must expand their marketing strategies, utilizing a mix of digital marketing, content creation, and targeted campaigns to amplify brand visibility. The goal is to capture the attention of a wider audience and solidify the brand's presence in the market.
Exploring New Customer Segments or Markets:
The Growth Stage invites entrepreneurs to explore new horizons. This may involve identifying untapped customer segments or venturing into new geographic markets. Diversifying the customer base helps mitigate risks associated with dependency on a single market segment.
Introducing New Features or Products:
Innovation is the lifeblood of the Growth Stage. Entrepreneurs should be proactive in identifying opportunities to introduce new features or products that align with the evolving needs and preferences of their target audience. This not only retains existing customers but also attracts new ones seeking cutting-edge solutions.
Adapting to Changing Market Demands:
Flexibility is a hallmark of successful startups in the Growth Stage. Entrepreneurs must remain agile and adaptive, responding swiftly to changing market demands. This may involve pivoting the business model, adjusting strategies, or incorporating feedback to stay aligned with the dynamic landscape.
Seeking Venture Capital or Strategic Partnerships:
Venture capital and strategic partnerships become integral components of the growth strategy. Entrepreneurs seek investors who share the vision and can provide not only capital but also valuable insights and networks. Strategic partnerships open doors to collaborative opportunities, market access, and shared resources.
Managing Financial Growth and Sustainability:
As the startup experiences exponential growth, managing finances becomes paramount. Entrepreneurs must strike a delicate balance between aggressive expansion and financial sustainability. Robust financial management practices ensure that growth is not only rapid but also sustainable in the long term.
Stage 5: Maturity and Expansion
This stage is characterized by market dominance, diversification, operational efficiency, and strategic maneuvers to secure a lasting position in the industry.
A. Market Dominance and Diversification:
Consolidating Market Share:
At the pinnacle of the Maturity and Expansion stage is the pursuit of market dominance. Startups consolidate their market share, solidifying their position as leaders in their industry. This involves strategic moves to outpace competitors, increase brand loyalty, and become the go-to choice for customers.
Exploring New Business Lines or Markets:
Beyond consolidation, startups in this stage explore new horizons for growth. This may involve diversifying into new business lines or entering untapped markets. By expanding the scope of offerings or venturing into complementary industries, startups can capture additional market share and mitigate risks associated with dependency on a single sector.
B. Operational Efficiency:
Streamlining Processes:
Operational efficiency becomes a key focus in the Maturity and Expansion stage. Startups analyze and optimize internal processes to eliminate inefficiencies, reduce costs, and enhance productivity. Streamlining operations ensures that the company is agile and responsive to market demands, laying the groundwork for sustainable growth.
Investing in Technology and Infrastructure:
As startups mature, the importance of technology and infrastructure investments becomes apparent. Entrepreneurs must leverage cutting-edge technologies to enhance efficiency, improve customer experiences, and stay ahead of industry trends. Strategic investments in infrastructure, whether digital or physical, support the scalability needed for expansion.
C. Strategic Partnerships and Acquisitions:
Collaborating with Industry Leaders:
Strategic partnerships are a powerful tool for startups in the Maturity and Expansion stage. Collaborating with industry leaders opens avenues for shared resources, expanded networks, and mutual growth. These partnerships can enhance credibility, provide access to new markets, and foster innovation through knowledge exchange.
Acquiring or Merging with Complementary Businesses:
Acquisitions and mergers are strategic moves that enable startups to strengthen their position in the market. By acquiring or merging with complementary businesses, startups can broaden their offerings, access new customer bases, and achieve economies of scale. This strategic expansion contributes to sustained success in the long term.
Startup Exit Strategy
Throughout these stages, the importance of having a well-crafted exit strategy cannot be overstated. As startups mature and evolve, founders and investors must keep the endgame in mind. Whether it's through an IPO, acquisition, merger, or management buyout, the exit strategy serves as the culmination of the entrepreneurial journey, providing a return on investment and ensuring the legacy of the startup.
In essence, the strategic considerations woven into the fabric of each startup phase contribute to the overall success and viability of the exit strategy. From the clarity of ideation to the financial acumen of the growth stage, every decision and action shapes the trajectory toward a well-planned and successful exit.
Types of Exit Strategies:
- Initial Public Offering (IPO):
Going public through an IPO is a dream for many startups. This strategic move not only raises substantial capital but also offers increased visibility and credibility in the market. However, IPOs are complex and demand meticulous preparation.
- Acquisition:
Being acquired by a larger company is a common exit strategy. This allows founders and investors to cash in on their hard work, and the acquiring company gains valuable assets, technology, or talent. Building strategic partnerships along the way can enhance the likelihood of a successful acquisition.
- Merger:
Merging with another company can be a strategic move, combining resources and expertise for mutual benefit. Mergers can lead to a stronger market position and increased competitiveness.
- Management Buyout:
In some cases, the existing management team might opt for a buyout. This can be a seamless transition, especially when the current leadership is passionate about the company's future.
Crafting Your Exit Strategy:
Define Your Goals: Clearly outline your personal and financial objectives. Whether it's maximizing profits, maintaining the company's mission, or ensuring the well-being of employees, understanding your goals is the first step.
Timing is Key: The timing of your exit is crucial. It's essential to strike a balance between leaving too early and potentially missing out on growth opportunities and waiting too long, risking a downturn in the market.
Maintain Flexibility: Markets are unpredictable, and circumstances change. Keep your exit strategy flexible, allowing for adjustments based on market conditions, industry trends, and the overall business landscape.
Communicate Effectively: Transparency is key when communicating your exit strategy to stakeholders. Keep your team, investors, and partners in the loop, ensuring a smooth transition and maintaining trust.
Conclusion
The entrepreneurial journey is a dynamic odyssey marked by distinct stages – ideation, seed, early traction, growth, and maturity. Each phase presents unique challenges and opportunities, demanding adaptability and strategic thinking. From defining ideas and forming teams to navigating growth and maturity, entrepreneurs shape their startups' trajectories.
The stages serve as roadmaps, guiding entrepreneurs through critical milestones. As startups evolve, they become agents of change, contributing to industries and communities. Success isn't just financial; it's about impact and innovation. The journey is continuous, offering lessons, victories, and resilience-building challenges.
In the tapestry of entrepreneurship, each startup writes a unique story. Through discovery, growth, and transformation, startups become architects of change, contributing to the dynamic landscape of innovation. In conclusion, may every startup find inspiration in its narrative, forging a path toward enduring success in the ever-evolving entrepreneurial terrain.

About Blockchain Founders Group
Blockchain Founders Group (BFG) is the driving force behind web3 innovation. As a company builder, we bring together a team of blockchain visionaries, experienced entrepreneurs, and industry experts, all committed to nurturing emerging talent. Our BFG acceleration programs serve as your springboard for launching blockchain startups, transforming concepts into reality in just 2-3 months. Each cohort develops 5-8 unique web3 ideas, and selected projects will be financially supported with 70,000 - 120,000 EUR, along with access to our extensive network. Join us in shaping the future of web3!
Stay updated by connecting with us on LinkedIn, Medium, Twitter, and YouTube.
Contact: Max Zheng, Director of Investments, max.zheng@blockchain-founders.io.
Subscribe by email
Share this
You May Also Like
These Related Stories

Becoming an entrepreneur and launching your crypto startup

What is a Startup Incubator? Everything You Need to Know

No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think